Efficient Method Development for the Analysis of Naphazoline Hydrochloride, Pheniramine Maleate, and Associated Related Substances Using a Systematic Screening Protocol
Abstract
A systematic screening protocol was used to develop an ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) method for the analysis of naphazoline hydrochloride (HCl) and pheniramine maleate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and their associated related substances. Following a predefined experimental plan, the major selectivity factors were systematically screened during the study, enabling efficient method development. An Arc™ Premier System integrated with a PDA detector and an ACQUITY™ QDa Mass Detector was used to develop a method. The Empower™ Chromatography Data System (CDS) enabled automated creation of chromatographic methods, peak tracking, data analysis, and reporting. The final method, operated under mass spectrometry (MS) compatible conditions, successfully separated all compounds producing a USP resolution ≥1.5 between all peaks and excellent repeatability of replicate injections.
Benefits
- Increase efficiency of the method development using a systematic screening protocol
- Automate creation of chromatographic methods, data analysis, peak tracking, and reporting with Empower 3 CDS tools
- Accurately identify components and confirm spectral peak purity using PDA and ACQUITY QDa Mass Detectors
Introduction
A systematic method development approach is based on the predefined set of objectives and experimental protocol.1 Key factors affecting selectivity and resolution are systematically evaluated throughout the process to generate the desired separation and resolution. Employing a systematic protocol enables fast and effective development of robust methods that reliably generate reproducible and accurate results.
Naphazoline HCl and pheniramine maleate are active ingredients found in the multi-component ophthalmic solutions used for the treatment of eye inflammation and allergic conjunctivitis.2 Many of the methods published in the literature are designed for analysis of individual API or lack specificity for impurities (or related substances). While the USP monograph for naphazoline hydrochloride and pheniramine maleate ophthalmic solution specifies procedure for API assay but lacks method for impurities.3 The USP monographs for naphazoline hydrochloride ophthalmic and nasal solutions also do not provide procedure for impurities.4,5 The European Pharmacopeia lists two separate methods for the related substances analysis of naphazoline HCl and pheniramine maleate, respectively.6,7
In this work, a systematic screening protocol is employed to develop a single LC method for the analysis of naphazoline hydrochloride and pheniramine maleate APIs and their associated related substances specified by the European pharmacopeia.6,7 The systematic protocol incorporates scouting, screening, and optimization steps. The Arc Premier System and Premier columns are used in the study. The Arc Premier System is equipped with a column manager and solvent select valve to maximize flexibility of the method development by automating the column and organic modifier switching. Both the UV and mass spectral data are utilized for accurate identification and tracking sample components during the study, as well as spectral peak purity verification. The developed method enables simultaneous determination of naphazoline hydrochloride and pheniramine maleate APIs and their associated related substances, suitable for analysis of multi-component drug product formulations.
Experimental
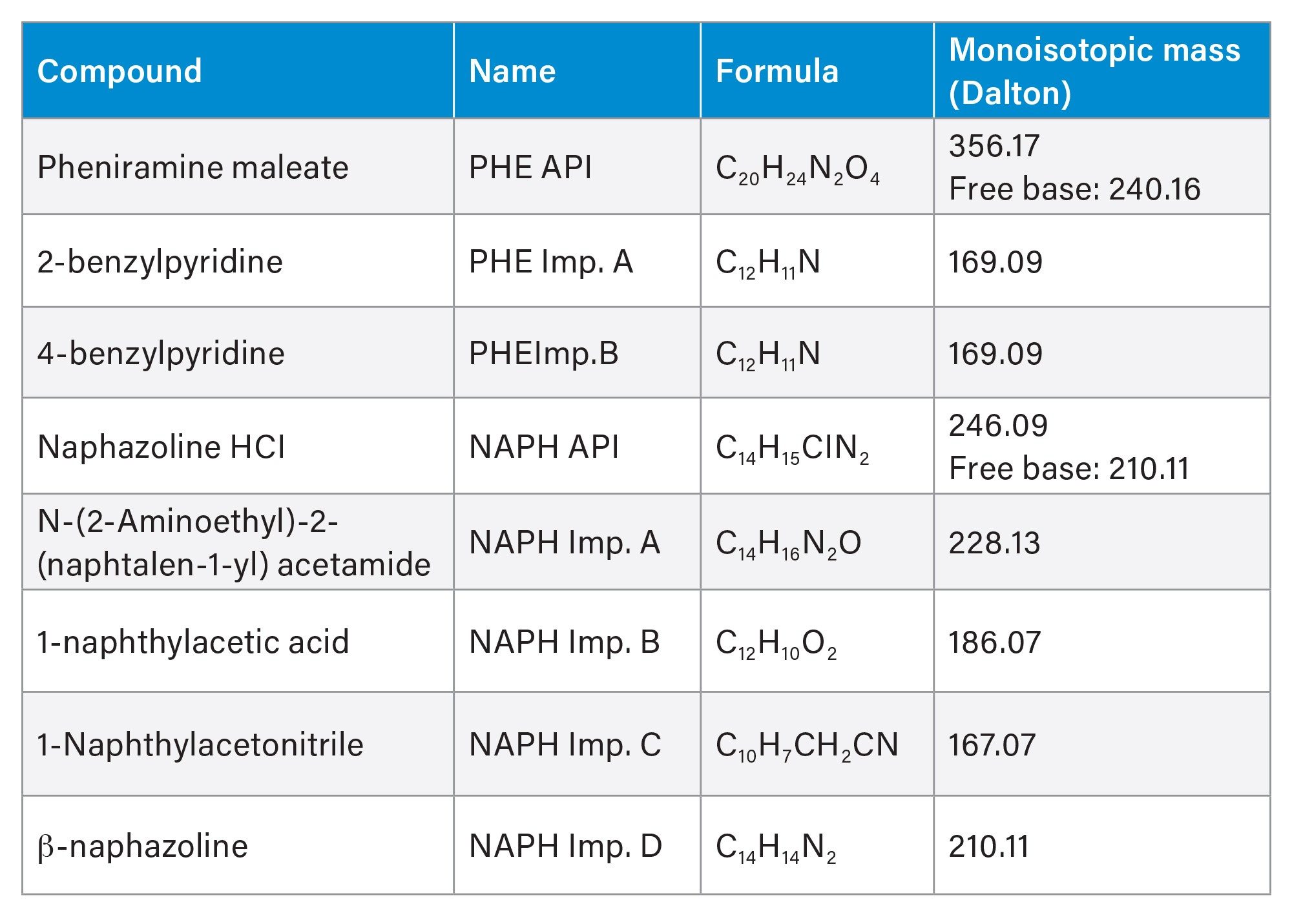
Compounds (Table 1) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich and Toronto Research Chemicals (TRC). Mass spectrometry grade reagents and solvents were obtained from Honeywell.
Sample Description
Standard solutions:
Individual stock solutions were prepared in methanol at 4.0 mg/mL. Stock solutions were diluted with 80:20 water/methanol diluent to make a mixture standard solution for method development containing naphazoline HCl and pheniramine maleate active ingredients at 0.5 mg/mL and related substances at 40 µg/mL. List of compounds for method development is shown in Table 1.
Ophthalmic Drug Product Solution
Over the counter (OTC) ophthalmic solution with pheniramine maleate 0.3% and naphazoline hydrochloride 0.025%
- Samples were prepared by dilution in the diluent (80:20 water/methanol) to the working concentration of approximately 500 µg/mL pheniramine maleate and 40 µg/mL naphazoline HCl.
LC Conditions
|
LC system: |
Arc Premier System, column manager with active pre-heating, PDA and ACQUITY QDa Detectors |
|
Vials: |
LCMS Maximum Recovery 2 mL volume, p/n: 600000670CV |
Method Development Conditions
|
Column(s): |
All columns 4.6 x 100 mm, 2.5 µm XSelect Premier CSH C18 (p/n: 186009873) XSelect Premier CSH Phenyl Hexyl (p/n: 186009890) XSelect Premier HSS T3 (p/n: 186009859) Atlantis Premier BEH C18 AX (p/n: 186009397) XBridge Premier BEH C18 (p/n: 186009848) |
|
Column temperature: |
40 °C |
|
Sample temperature: |
10 °C |
|
Injection volume: |
5.0 µL |
|
Flow rate: |
1.0–1.5 mL/mim |
|
Mobile phase: |
A: 1% Formic acid in water B: 1% Ammonium hydroxide in water C: Water D1: Acetonitrile D2: Methanol |
|
Gradient: |
Slope: 5 to 90, 80, 70, 60% organic over 10 minutes Time: 5 to 90% organic over 10, 11, 12, and 13 minutes |
|
Wash solvents: |
Purge/Sample Wash: 50:50 water/methanol Seal Wash: 90:10 water/acetonitrile |
|
Detector settings: |
PDA: 210–400 nm (derived at 260 nm) |
Final Method Conditions
|
Detection: |
UV at 260 nm |
|
Column(s): |
XSelect Premier CSH C18, 4.6 x 150 mm, 2.5 µm (p/n: 186009874) |
|
Column temperature: |
42 °C |
|
Sample temperature: |
10 °C |
|
Injection volume: |
5.0 µL |
|
Flow rate: |
1.1 mL/min |
|
Mobile phase A: |
0.1% Formic acid in water |
|
Mobile phase B: |
0.1% Formic acid in methanol |
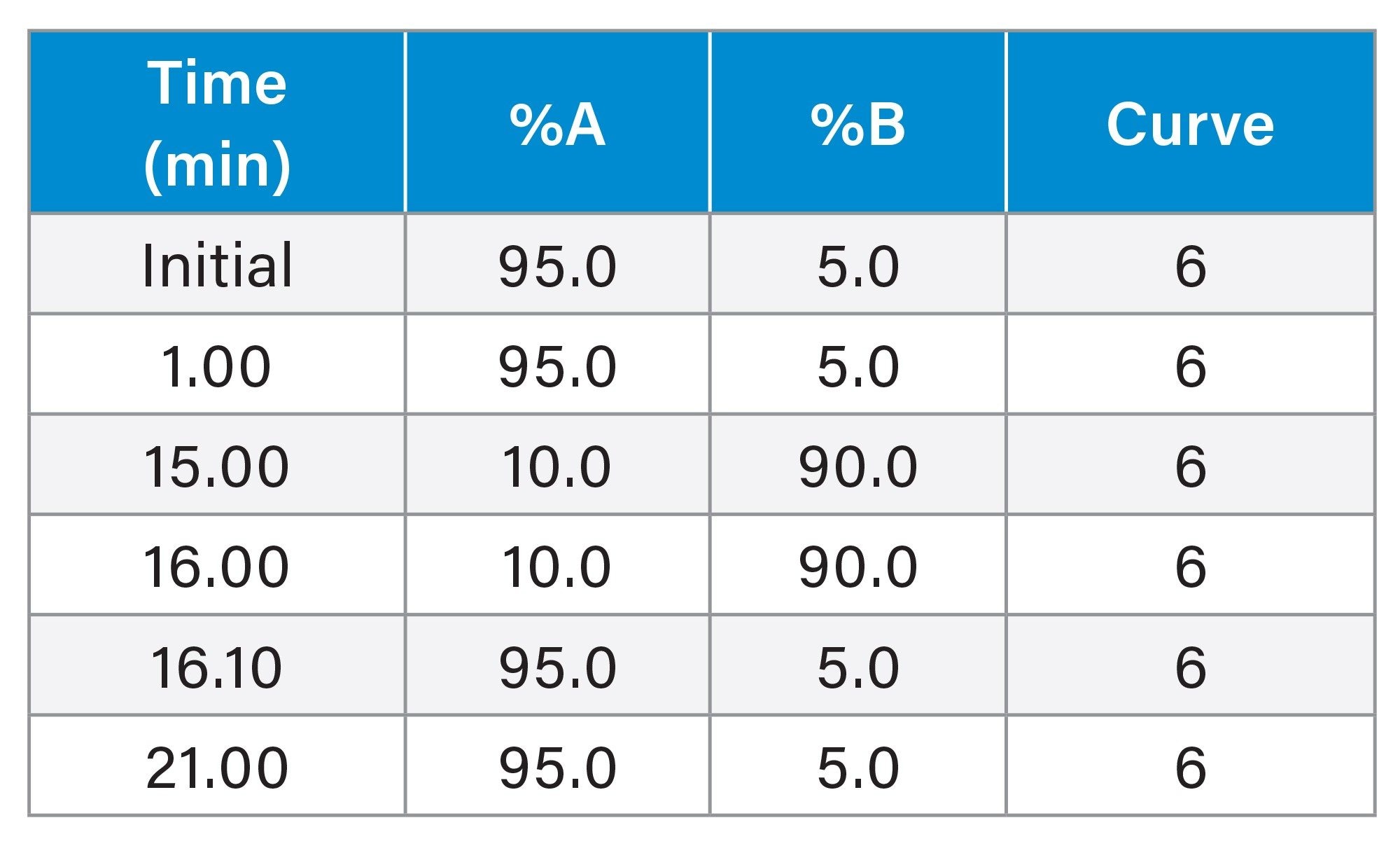
Gradient Table
MS Conditions
|
MS system: |
ACQUITY QDa Mass Detector |
|
Ionization mode: |
Positive and negative |
|
Acquisition range: |
50–250 Da |
|
Capillary voltage: |
0.8 kV |
|
Cone voltage: |
2 V |
Data Management
|
Chromatography software: |
Empower 3 FR5 SR5 |
Results and Discussion
Method Development
Systematic Screening Protocol
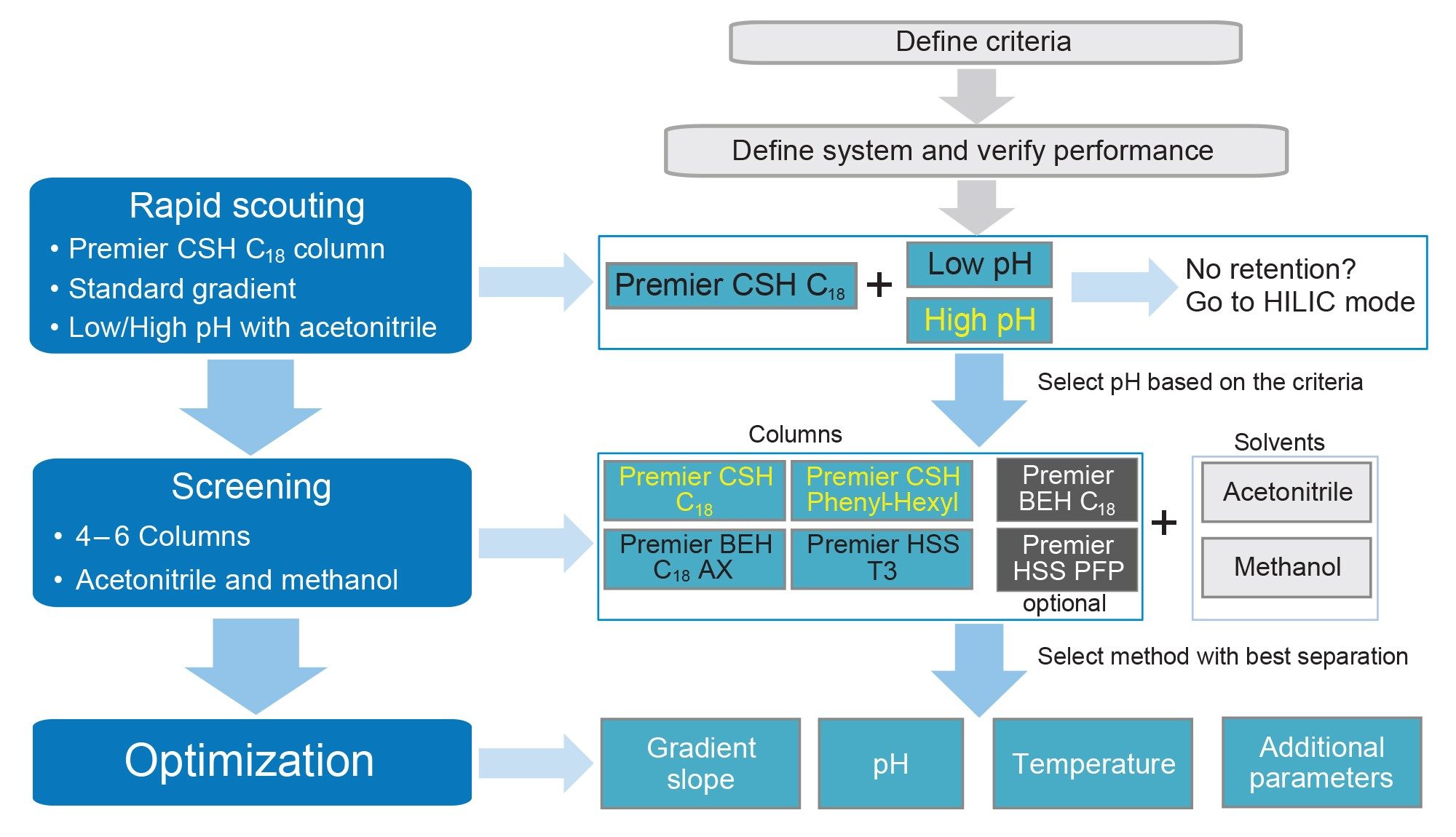
A UHPLC method for the analysis of naphazoline HCl, pheniramine maleate, and their associated related substances was developed following a systematic screening protocol (Figure 1). The protocol begins with the definition of the separation criteria and chromatographic system, followed by the experimental study. The method development study incorporates rapid scouting, screening, and optimization steps. The major selectivity factors including pH, column chemistry, and organic modifier are systematically evaluated during the process to achieve the desired separation. Results from each step of the method development are assessed against the specific criteria. The best method is selected and further optimized to meet the predefined performance acceptance criteria.
The separation criteria for naphazoline HCl, pheniramine maleate, and their associated related substances included USP resolution of ≥1.5 between the peaks, peak tailing of ≤1.5, and retention factor (k*) ≥2.0. The Arc Premier System configured with a column manager and solvent select valve was chosen for the study, allowing automated column and organic modifier screening. The system was integrated with the ACQUITY QDa and PDA detectors, enabling quick identification of the sample components and peak purity confirmation.
Rapid Scouting
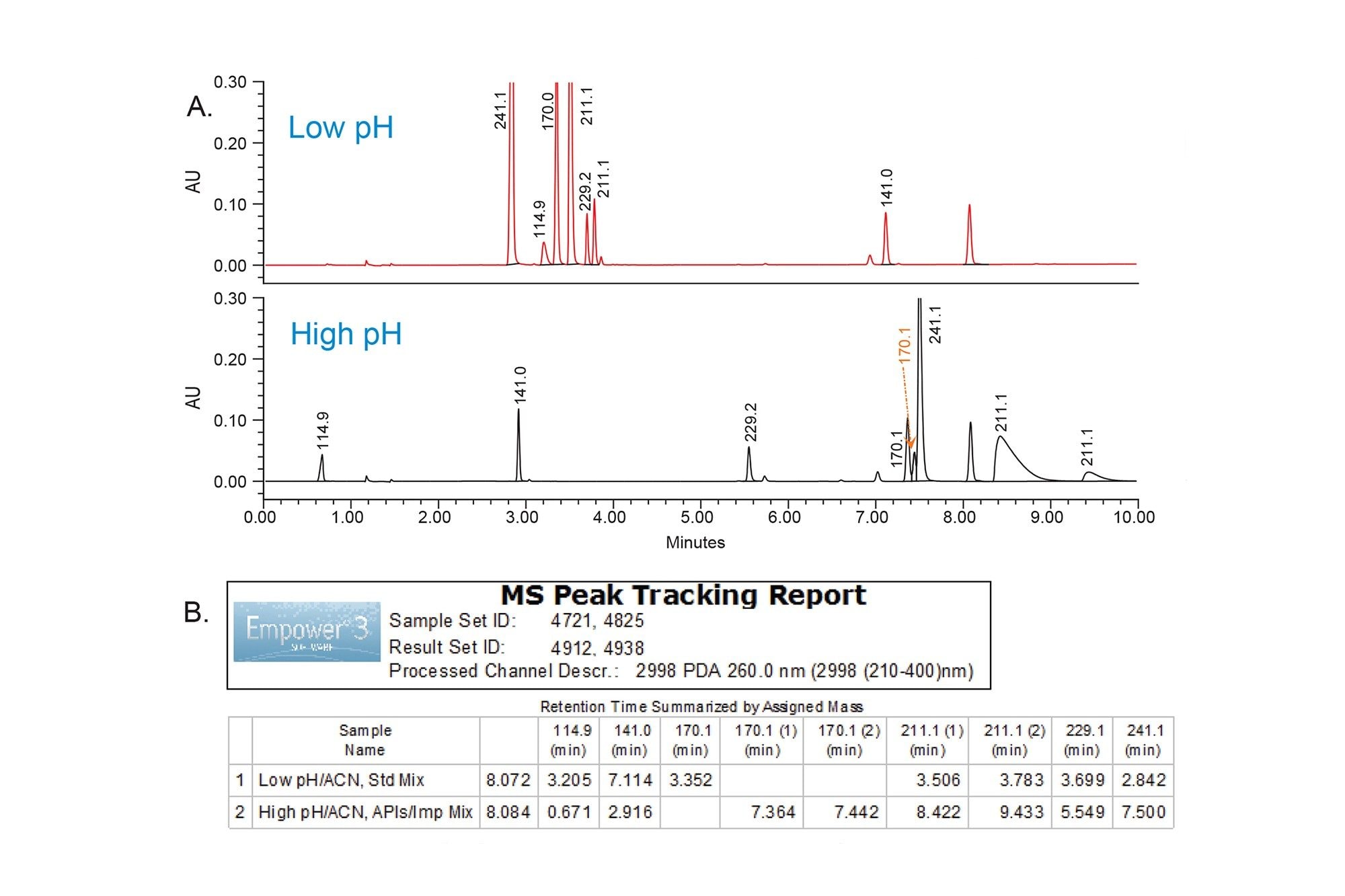
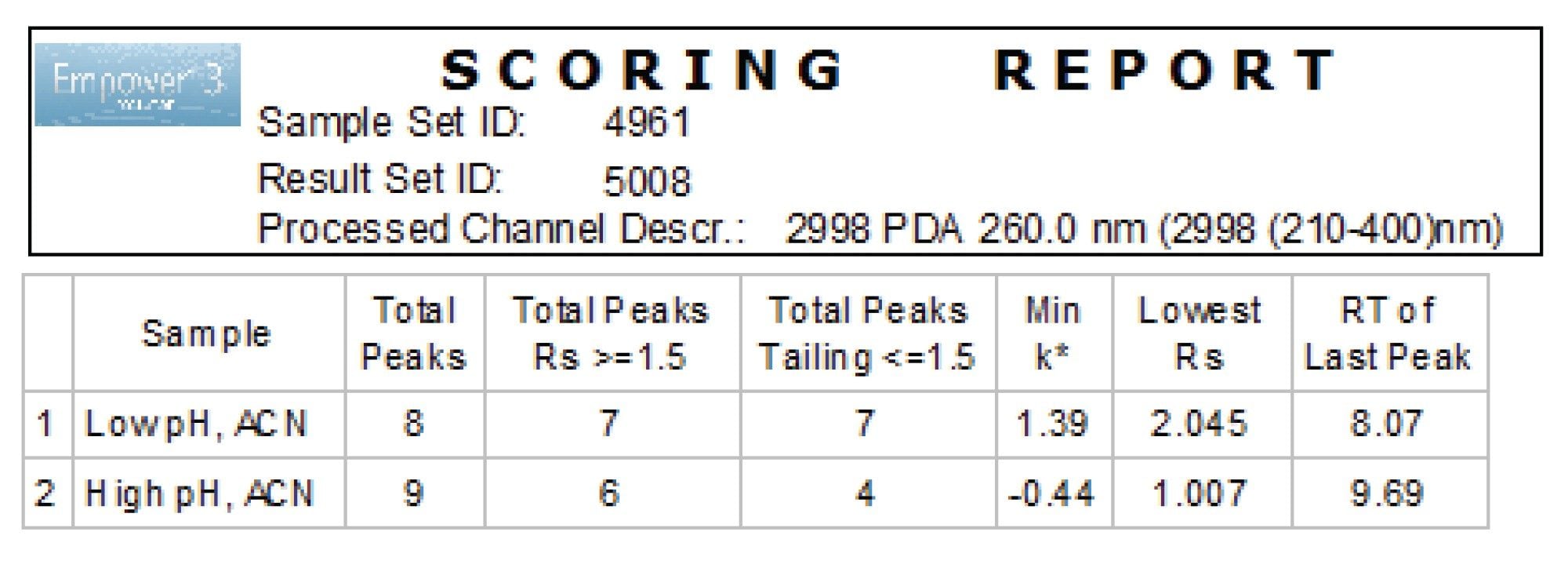
The goal of the rapid scouting was to quickly identify separation condition for best retention of the analytes. The XSelect Premier CSH C18 Column was used to perform low and high pH experiments using stock solutions of 125 mM formic acid and 125 mM ammonium hydroxide with a gradient of 5–90% acetonitrile over 10 minutes. The chromatographic retention of the analytes under low and high pH conditions was tracked using mass data from the ACQUITY QDa Detector by mass-to-charge (m/z) ratio (Figure 2). The data was processed in Empower automatically using ApexTrack integration to detect peaks. The MS peak tracking processing and reporting in the Empower 3 Software was used to monitor elution order of each analyte over the pH experiments. The MS peak tracking report displayed the retention time for each peak with a specific m/z value over the chromatographic runs (Figure 2B). An additional peak with m/z 114.9 observed under low and high pH conditions was found to be a maleate salt, separated from the free base pheniramine peak. Some analytes shared the same masses including naphazoline API and naphazoline impurity D (m/z 211.1), as well as pheniramine impurity A and impurity B (m/z 170.1). The naphazoline impurity C compound was not detected by an ACQUITY QDa, hence no mass spectral data was available for this compound.
The Empower custom scoring report facilitated selection of the conditions by identifying the total number of peaks that met the separation goals (Figure 3). The low pH condition provided best retentivity and separation for all analytes, hence was chosen for screening phase of the method development study.
Screening
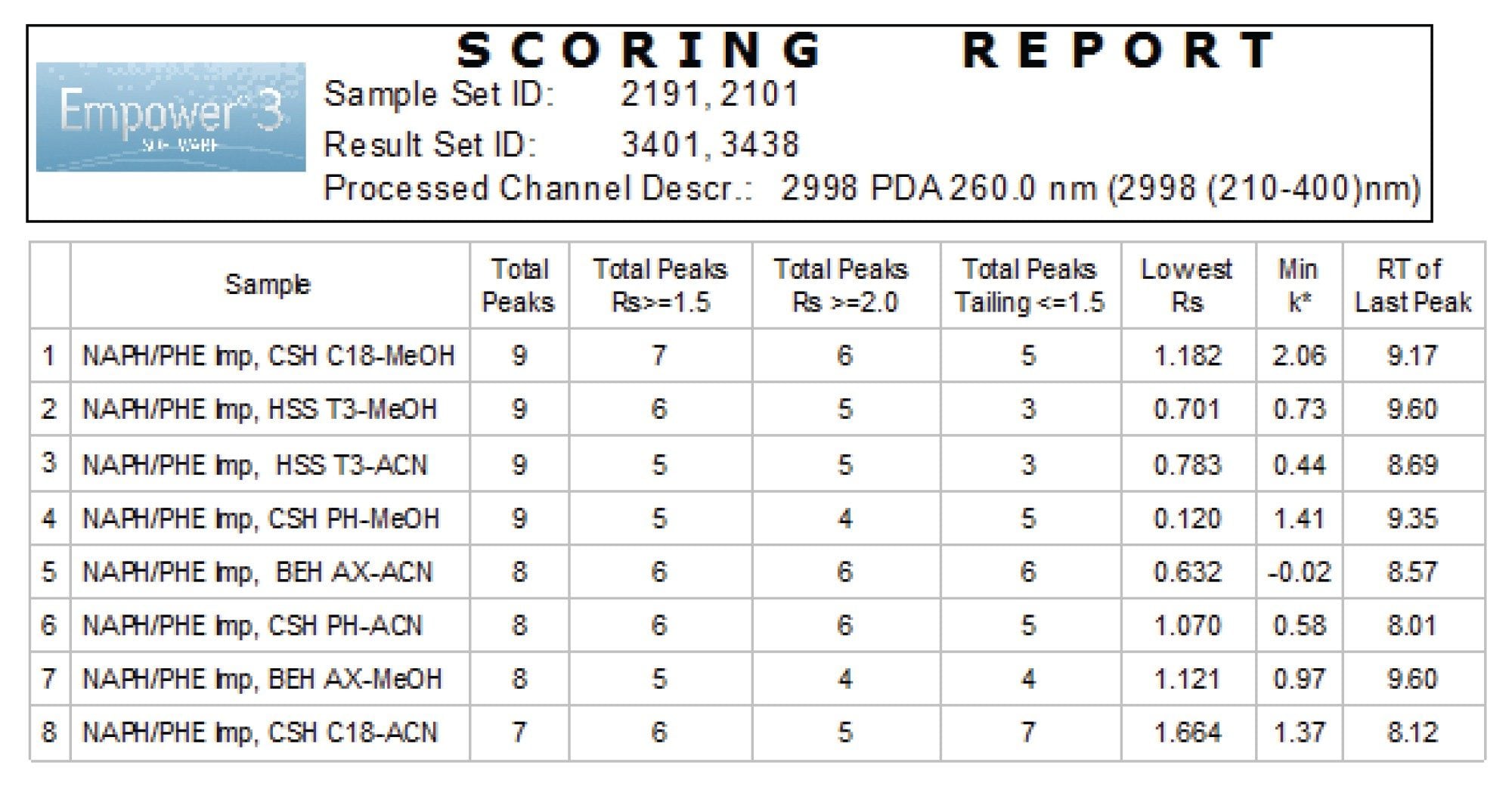
Operating under low pH, the MaxPeak Premier Columns were screened with acetonitrile and methanol organic modifiers. Different base particles and stationary phase were chosen to provide a wide range of selectivity. The column manager integrated with switching valves automated columns screening, eliminating need for user intervention. The separation was performed using the same gradient as in a rapid scouting step. The chromatographic methods required to run the entire study were created using the Empower Sample Set Generator (SSG)8. The Empower SSG automated the creation of instrument methods, method sets, and sample set method, while varying the chromatographic parameters. The scoring report indicated that the Premier CSH C18 and methanol solvent provided best separation with largest number of peaks with resolution of ≥1.5 and peak tailing less than 1.5 (Figure 4).
Optimization
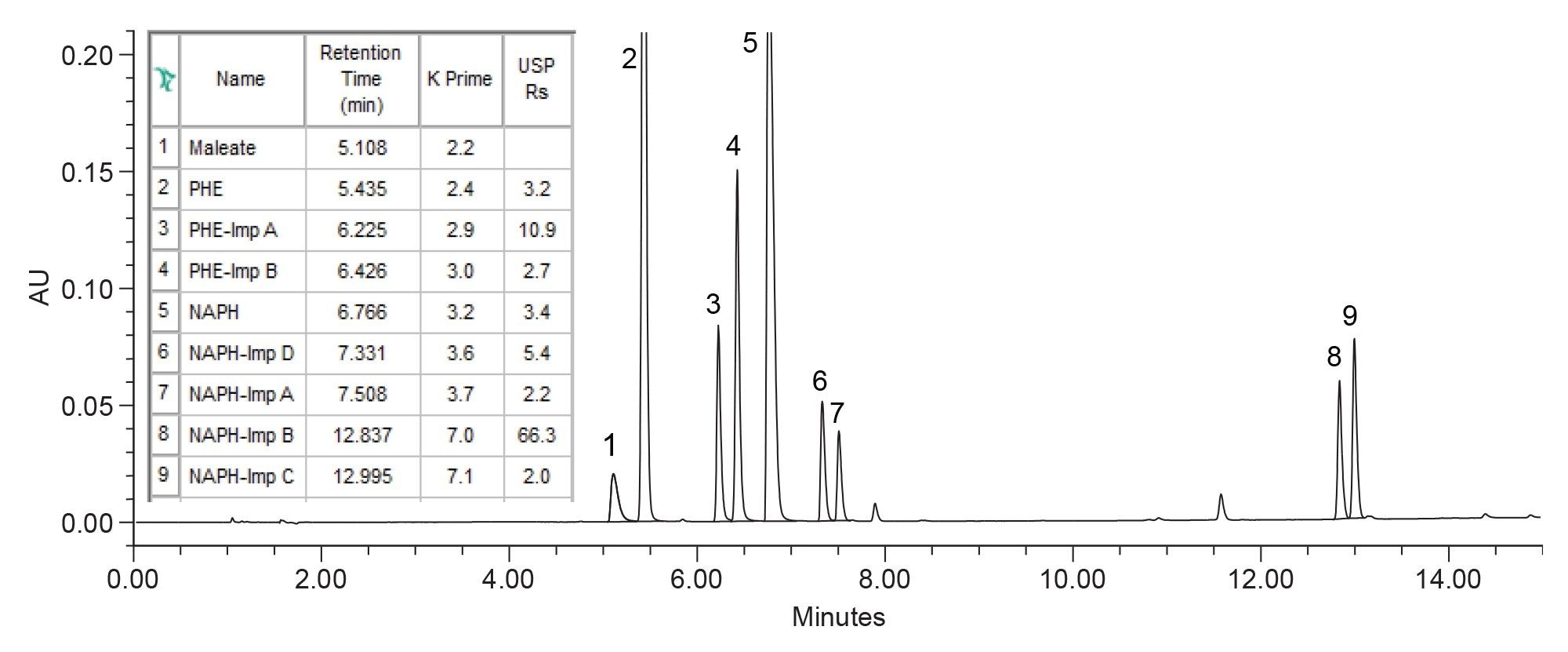
The method with Premier CSH C18 and methanol was further optimized to ensure that all the separation criteria are met. The chromatographic parameters adjusted in the optimization included gradient time, gradient slope, pH, column temperature, flow rate, and column length. Increasing the column length, while maintaining the same particle size of 2.5 µm met the separation goals for resolution of ≥1.5 between all peaks (Figure 5). The optimized method produced excellent separation between related substances and the highly concentrated pheniramine and naphazoline active ingredients. Ensuring separation between the API peak and the impurities is critical as impurities assay methods often require test sample preparation with high concentration of the active ingredient to detect low-level impurities.
System Suitability
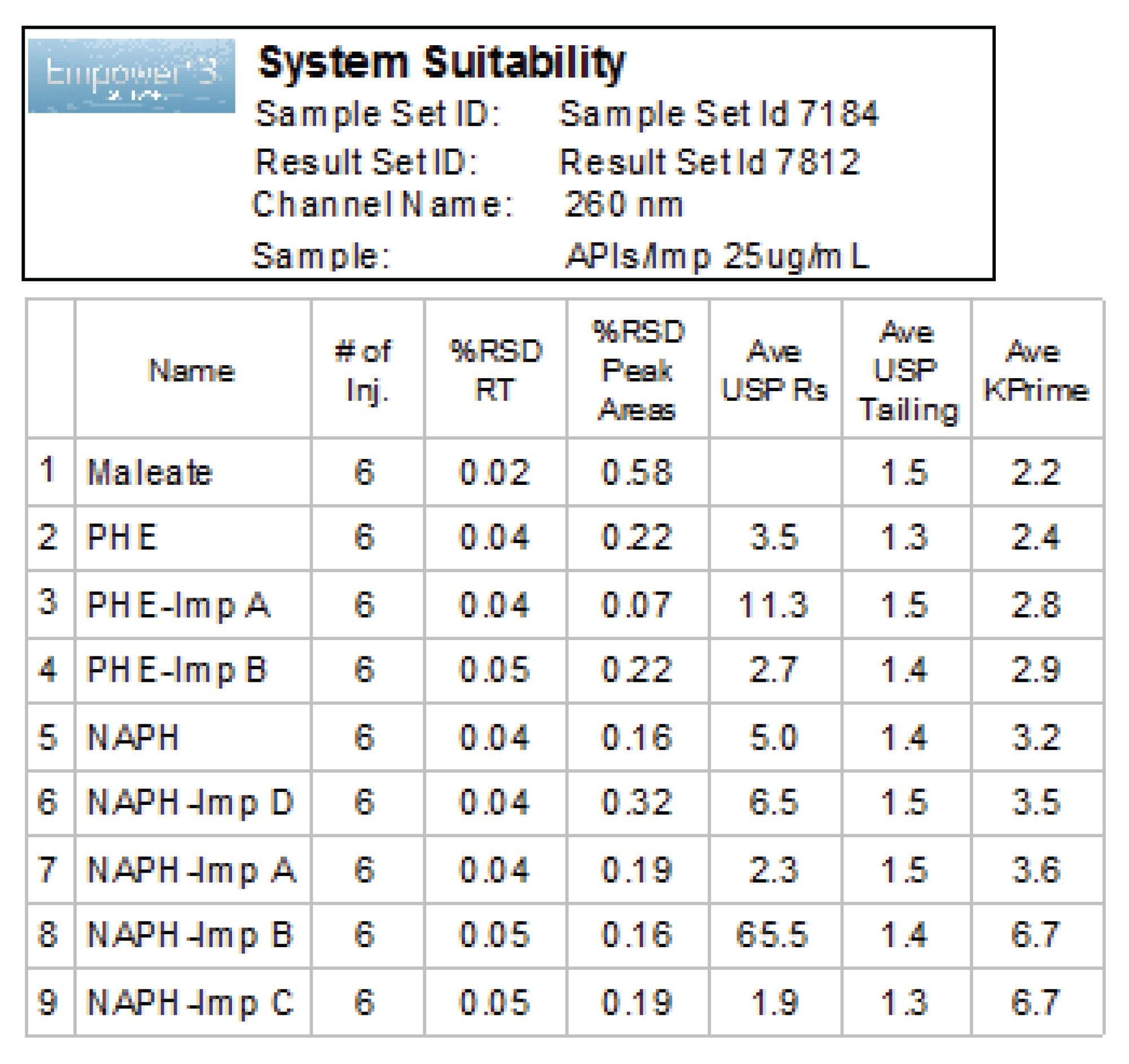
System suitability results for six replicate injections showed excellent repeatability of the retention times and peak areas (Figure 6). The relative standard deviation (RSD) for peak areas and retention times were ≤0.58% and ≤0.05%, respectively.
Analysis Of Ophthamlic Solution
The ophthalmic solutions containing pheniramine maleate and naphazoline HCl APIs were analyzed to demonstrate that the developed method can separate all analytes from the formulation excipients. This is consistent with method specificity and often done by verifying spectral purity of the chromatographic peaks.
In this work, UV and mass spectral data were used to confirm spectral homogeneity of the analytes in the ophthalmic solution formulation containing 500 µg/mL pheniramine maleate and 40 µg/mL naphazoline HCl (Figure 7). The Empower peak table showed that the purity angle for each analyte was below the threshold angle, confirming spectral homogeneity (Figure 7A). This was also visually examined using a UV purity plot as demonstrated for naphazoline impurity A (Figure 7B). Additionally, the Empower 3 Mass Analysis with purity spectrum showed one mass across the entire peak (leading, apex, and trailing edge) with m/z of 229.1, which is specific to naphazoline impurity A (Figure 7C). Using both the UV and MS spectral data enabled spectral homogeneity confirmation to ensure that analytes are not subject to interference with any excipients of the sample formulations.
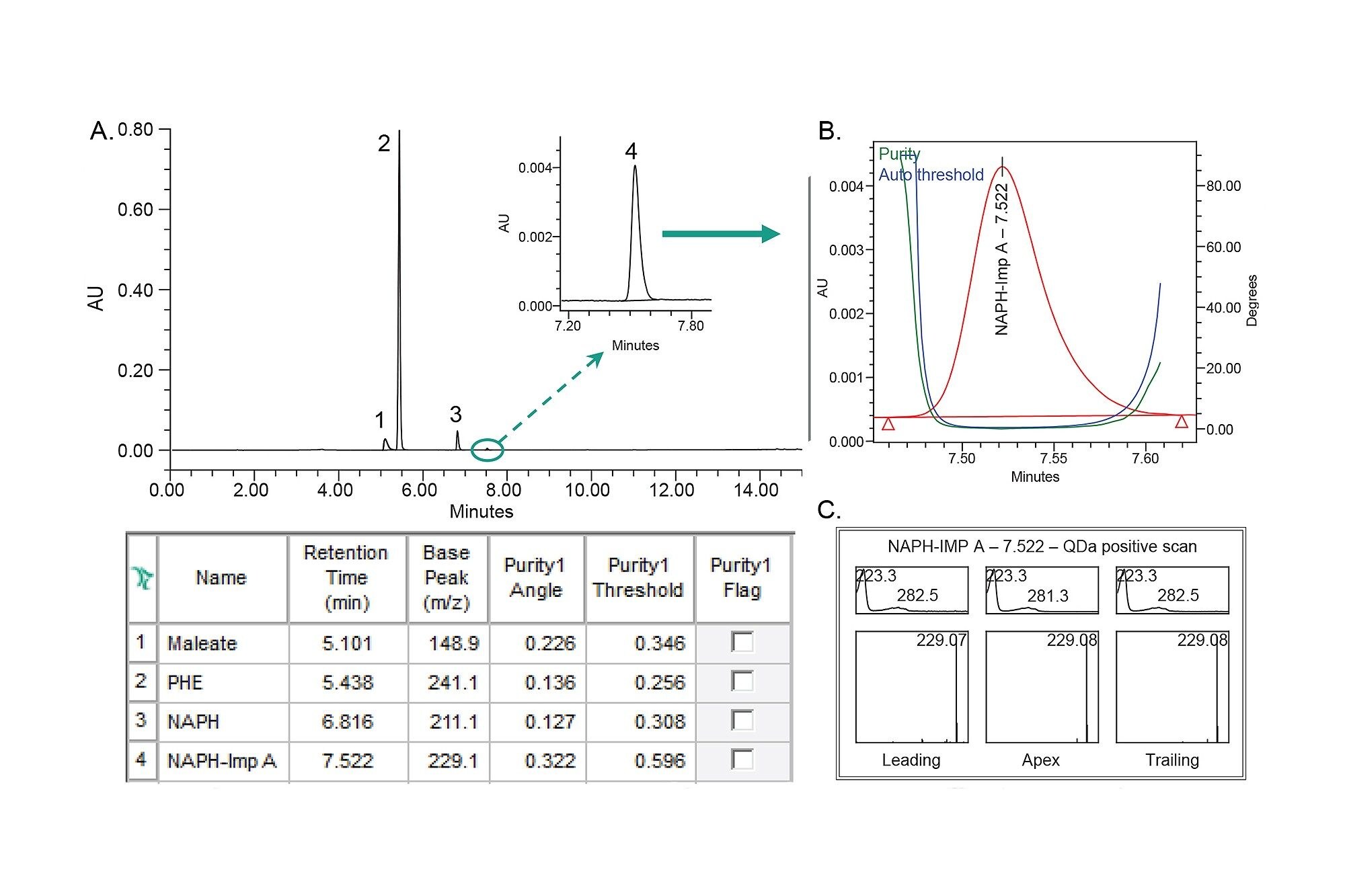
Conclusion
A single UHPLC method was successfully developed for the simultaneous determination of naphazoline HCl and pheniramine maleate APIs and their associated related substances, utilizing a systematic screening protocol. The Arc Premier System with a column manager and solvent select valve automated screening of multiple columns and mobile phases in one chromatographic run. The ACQUITY QDa Detector in conjunction with UV detection enabled quick identification of sample components, elution order tracking and spectral peak purity confirmation. The Empower software provided automated peak detection, data analysis, and reporting.
Utilizing a predefined systematic screening protocol and Empower CDS enables faster and more effective development of robust methods that reliably generate reproducible and accurate results, increasing the success of method validation and transfer across laboratories.
References
- Hong P, McConville P. A Complete Solution to Perform a Systematic Screening Protocol for LC Method Development. Waters White Paper, 720005268, 2018.
- https://www.webmd.com/drugs/2/drug-2734/naphazoline-pheniramine-ophthalmic-eye/details.
- USP Monograph, Naphazoline Hydrochloride and Pheniramine Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, USP40-NF35, The United States Pharmacopeia.
- USP Monograph, Naphazoline Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution, USP40- NF35, The United States Pharmacopeia Convention, official December 2017. 3.
- USP Monograph, Naphazoline Hydrochloride Nasal Solution, USP40-NF35, The United States Pharmacopeia Convention, official December 2017. 2.
- European Pharmacopeia Monograph, Naphazoline Hydrochloride, European Pharmacopeia 10.0, released January 2009. or 01/2009:0730.
- European Pharmacopeia Monograph, Pheniramine Maleate, European Pharmacopeia 10.0, released January 2009. or 01/2009:1357 .
- Maziarz M, Rainville PD. Automated Creation of Chromatographic Methods for Analysis with an ACQUITY QDa Detector Using Empower Sample Set Generator. Waters Application Brief, 720007775, 2022.
720007850, January 2023