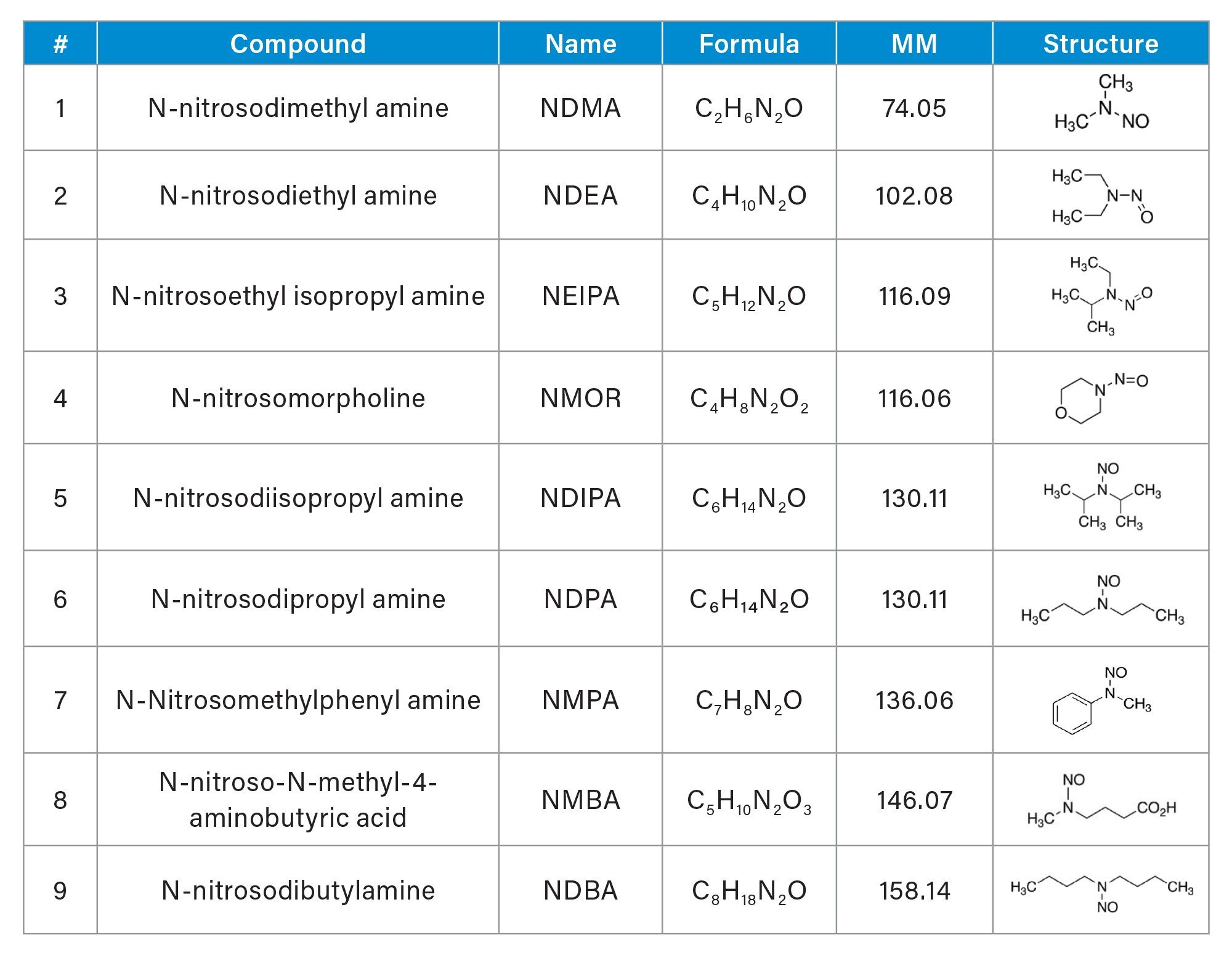
High Sensitivity Quantification of Nitrosamines in Metformin Using Xevo™ TQ Absolute Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer With an ACQUITY™ Premier System
Abstract
The presence of nitrosamine impurities in the pharmaceutical products pose significant risk to human health and must be monitored at the sub-ng/mL using highly sensitive and selective analytical methodologies. This work highlights the development and performance of an Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC™) method with tandem quadrupole mass spectrometer for the detection and quantification of nine nitrosamine impurities (NDMA, NDEA, NEIPA, NMOR, NDIPA, NDPA, NMPA, NMBA, NDBA) in metformin drug substance. The chromatographic separation was performed with an Atlantis™ Premier™ BEH C18 AX Column. Sensitive and accurate quantification was achieved using the ACQUITY Premier System with the Waters Xevo TQ Absolute Mass Spectrometer. The limits of quantification (LOQ) for nitrosamines ranged from 0.01 to 0.1 ng/mL in neat solvent and from 0.025 to 0.1 ng/mL metformin drug substance, respectively. Accurate quantitative performance was achieved at the 0.025 ng/mL (or 0.00125 ppm relative to 20 mg/mL metformin drug), with recoveries of 85–110%.
Benefits
- Trace level detection of nitrosamines in the metformin drug substance using Xevo TQ Absolute Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer in MRM acquisition mode
- Robust separation of nitrosamines and metformin drug using the Atlantis Premier BEH C18 AX Column with the ACQUITY Premier System
- Precise, repeatable, linear, and accurate quantitative performance for nitrosamines in the metformin drug substance
Introduction
Nitrosamine impurities are considered probable human carcinogens or compounds that can cause cancer.1,2 Since 2018, the discovery of nitrosamines in several marketed medicines resulted in disruptive product recalls, including angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), histamine blocker ranitidine (Zantac), and later expanded to metformin.3,4 To control the presence of nitrosamines in pharmaceuticals, the U.S. FDA and European Medicine Agency (EMA) established acceptable daily intake limits (nanograms/day) for nitrosamines in drug products.4,5 These limits are used to determine the threshold concentration for nitrosamines in a given product based on the recommended maximum daily dose.
Metformin is a prescription medication used for the treatment of high blood sugar in patients with type 2 diabetes.3 Several metformin dug products were recalled due to the presence of NDMA above the acceptable intake limit of 96 nanograms per day.3
Measuring of nitrosamines at the regulatory permitted threshold levels relies on highly sensitive and selective analytical methods. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) instrumentation have successfully been employed for the accurate identification and quantification of low-level nitrosamines in various pharmaceutical products.6,7
The UPLC-MS/MS method presented in this work provides a highly sensitive and selective detection and quantification of nine nitrosamines (Table 1) in metformin drug substance or active pharmaceutical ingredient (API). The developed method employs the Xevo TQ Absolute Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer and an ACQUITY Premier System. Method performance characteristics including limits of detection and quantitation (LOD and LOQ), reproducibility, linearity, and accuracy in metformin drug substance are demonstrated in this work.
Experimental
Nitrosamines standards were purchased from Toronto Research Chemicals (TRC) and Sigma-Aldrich. Mass spectrometry grade ammonium formate, solvents, and formic acid were obtained from Honeywell. Metformin drug substance was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
Standard Solutions in Neat Solvent
Individual stock standard solutions containing 5.0–10 mg/mL of each nitrosamine were used to make a mixture standard solution with nine nitrosamines at 100 µg/mL in methanol. The mixture standard solution was serially diluted with water to prepare LOD, LOQ, and linearity standard solutions.
Metformin Drug Substance (DS)
Metformin drug substance sample solutions were prepared in water at 20 mg/mL and filtered using 0.2 µm PVDF syringe filters (p/n: WAT200806) prior to analysis
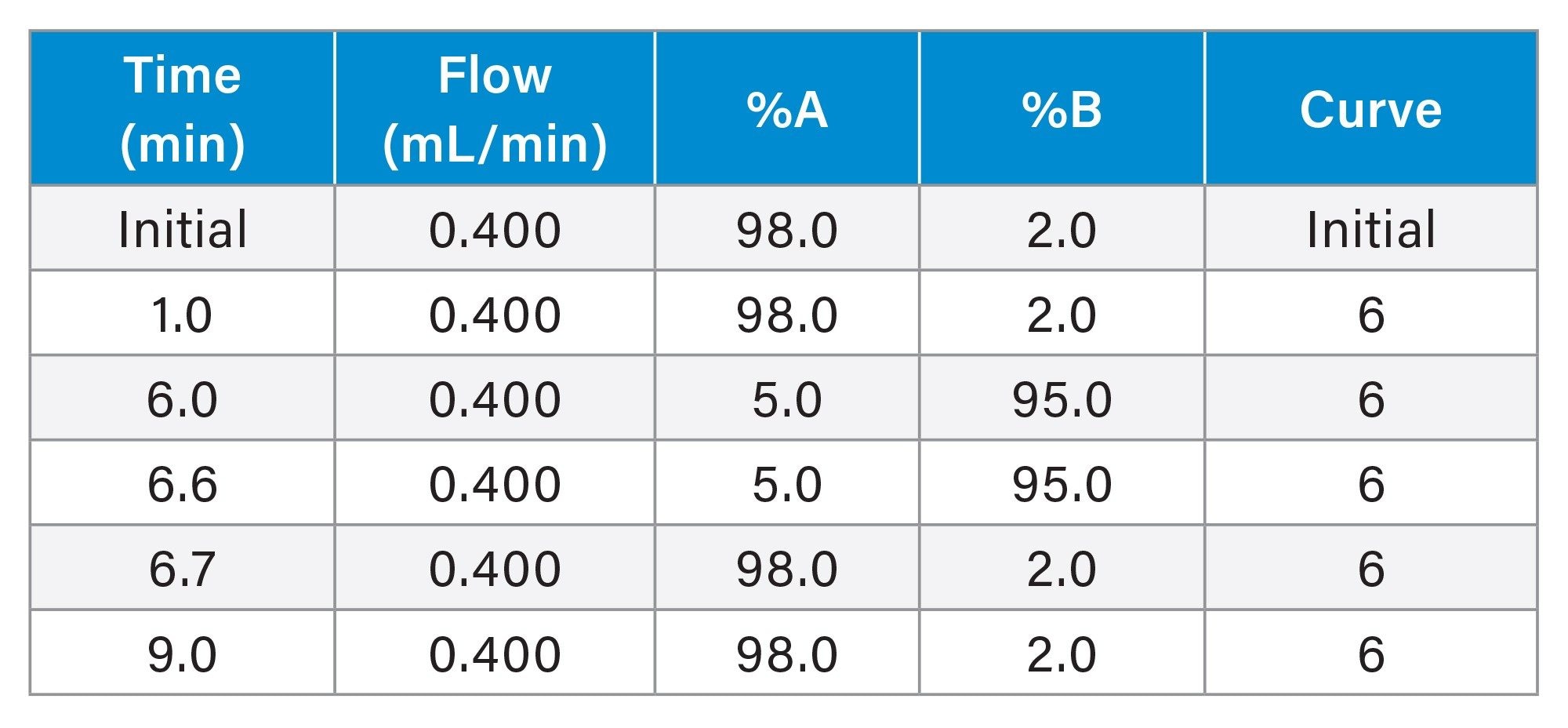
LC Conditions
|
LC system: |
ACQUITY™ Premier System |
|
Detection: |
MS/MS |
|
Vials: |
LCMS Maximum Recovery 2 mL volume, p/n: 600000670CV |
|
Column(s): |
Atlantis™ Premier BEH C18 AX (2.1 x 100, 1.7 um), p/n: 186009368 |
|
Column temp.: |
40°C |
|
Sample temp.: |
10°C |
|
Injection volume: |
30.0 µL |
|
Flow rate: |
0.4 mL/min |
|
Mobile phase A: |
5 mM Ammonium formate in water with 0.1% formic acid |
|
Mobile phase B: |
5 mM Ammonium formate in methanol with 0.1% formic acid |
|
Gradient: |
Described in gradient table |
Gradient Table
MS Conditions
|
MS system: |
Xevo™ TQ Absolute Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer |
|
Ionization mode: |
APCI+ |
|
Acquisition: |
MRM mode, described in Table 2 |
|
Corona: |
2.5 (µA) |
|
APCI probe temp.: |
325°C |
|
Desolvation gas glow: |
950 L/Hr |
|
Cone gas flow: |
300 L/Hr |
|
Nebulizer: |
300 L/Hr |
|
Collision gas flow: |
0.20 mL/Min |
|
Source Temp.: |
150°C |
Data Management
|
Data Management: |
Instrument control: MassLynx™ v4.2 |
|
Data processing: TargetLynx™ |

Results and Discussion
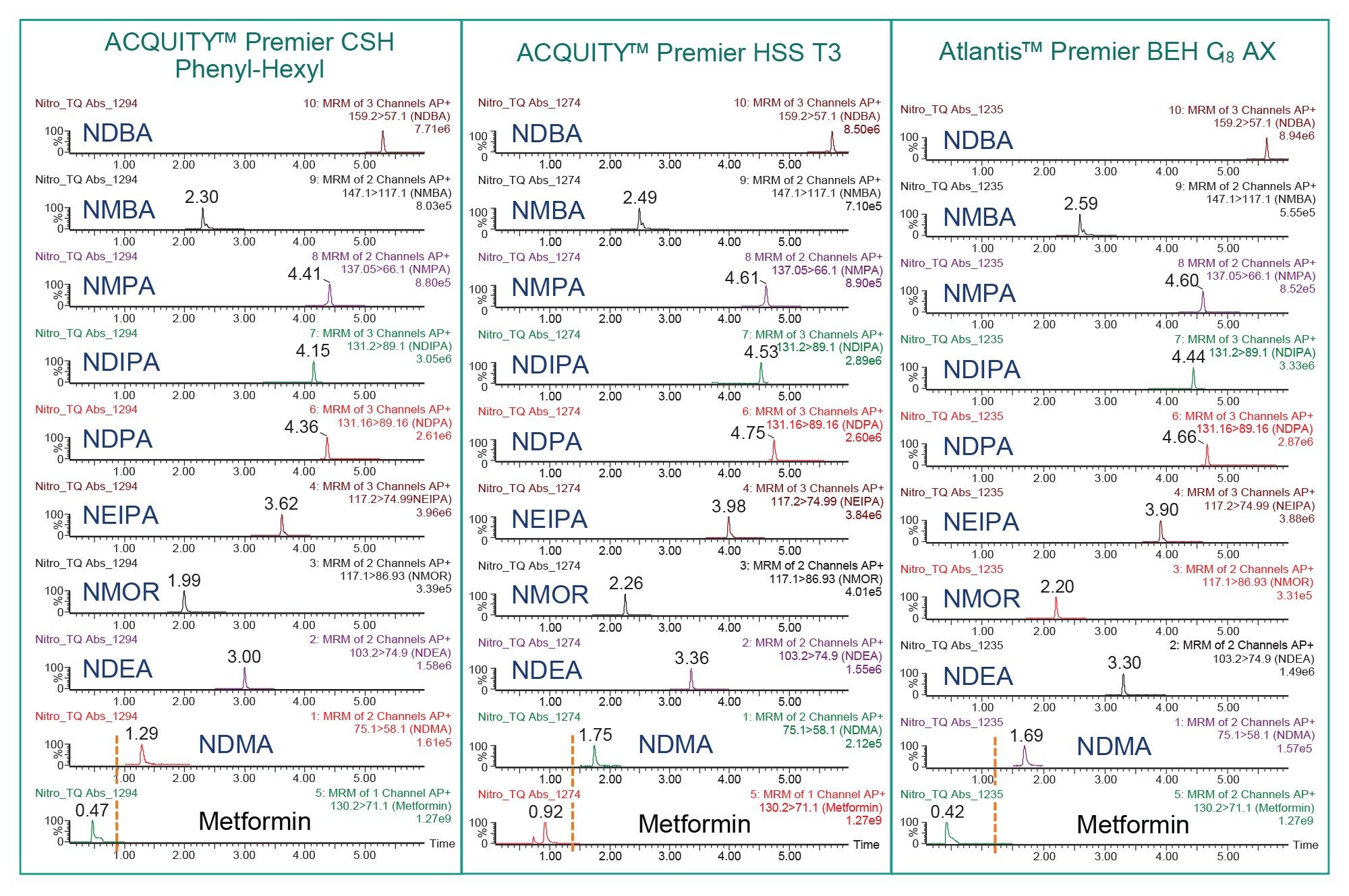
Various column chemistries were explored during the method development to ensure chromatographic separation for all nitrosamines, most importantly between the highly concentrated metformin API peak and the most polar NDMA peak. Ensuring separation between the concentrated API peak and the low-level impurities allows for the integration of the divert valve to direct API to waste, while directing the impurities into MS for analysis. Diverting API to waste minimizes the potential for matrix impacting ion suppression or enhancement on the trace level impurities.
Column screening for analysis of nitrosamines and metformin is shown in Figure 1. To assess the elution of the metformin peak, MS trace was acquired without the divert valve using a sample containing 10 ng/mL metformin drug substance with 1 ng/mL nitrosamines. While both the ACQUITY Premier HSS T3 and ACQUITY CSH™ Phenyl Hexyl provided adequate retention for all nitrosamines, the ACQUITY Atlantis Premier BEH C18 AX provided best chromatographic separation between metformin and NDMA (Figure 1). Additionally, the BEH C18 AX Column facilitated resolution between closely eluting nitrosamines including NDPA, NDIPA, and NMPA.
The atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) in positive mode was used for the detection and quantitation of nitrosamines based on the previous work for analysis of six nitrosamines including NDMA, NDEA, NEIPA, NDIPA, NDBA, and NMBA8. The MRM transitions and MS ionization parameters for nitrosamines were developed using IntelliStart™ functionality within the MassLynx Software.
Quantification in Neat Solvent
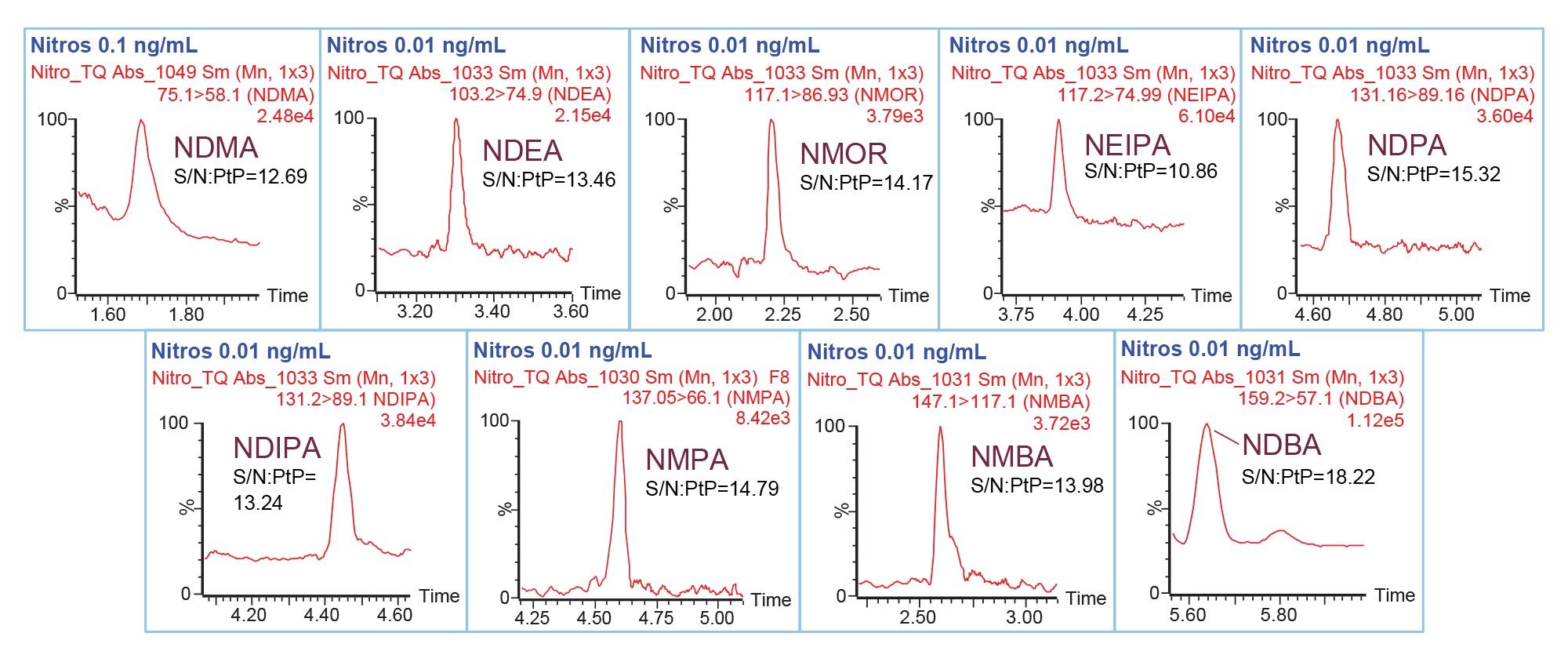
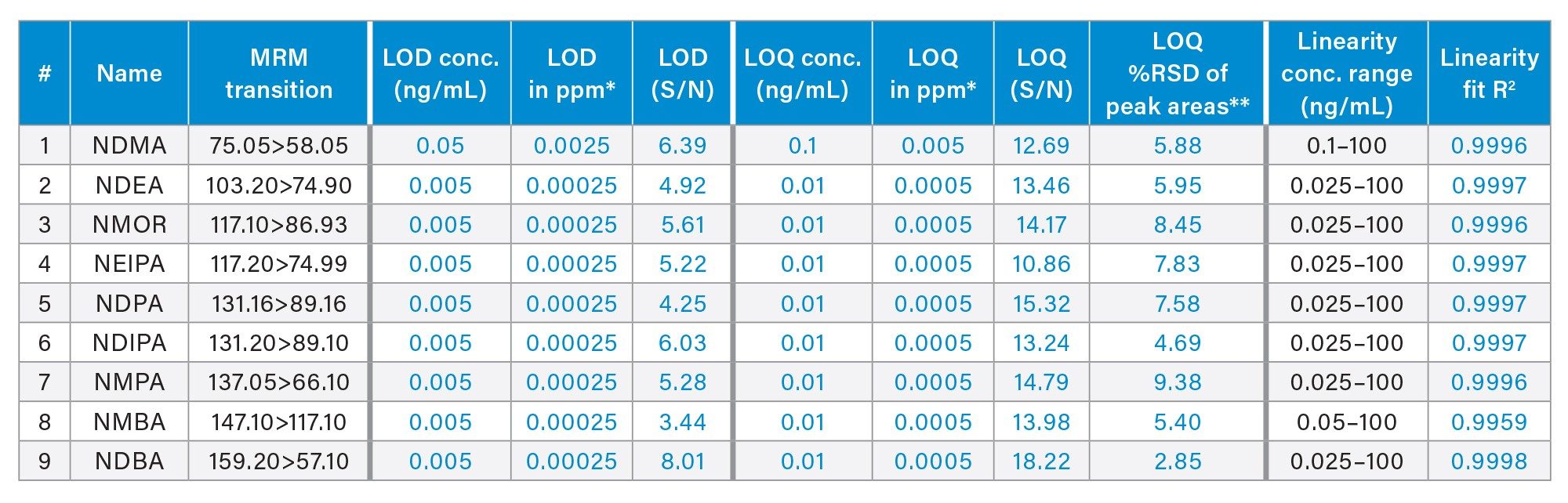
The LOD and LOQ for nitrosamines achievable with the UPLC-MS/MS method were determined following the signal-to-noise (S/N) criteria of 3:1 and 10:1, respectively. Representative chromatograms of the LOQ solutions in neat solvent are shown in Figure 2. Method performance characteristics including LOD, LOQ and linearity are summarized in Table 3. The LOD and LOQ for NDMA was found to be 0.05 and 0.1 ng/mL, respectively. Furthermore, LOD and LOQ of 0.005 and 0.01 ng/mL were achieved for NDEA, NMOR, NEIPA, NDPA, NDIPA, NMPA, NMBA, and NDBA. The LOQ of 0.1 and 0.01 ng/mL correspond to 0.005 and 0.0005 ppm with respect to the 20 mg/mL of metformin drug substance. Excellent performance at the LOQ levels was achieved for nitrosamines with the relative standard deviation (RSD) of the peak areas less than 10% based on data from six replicate injections (Table 3). No internal standard was used in this work to correct for data variability. Additionally, the method exhibited a linear relationship between the MS responses and concentrations with the correlation coefficients of ≥0.996 (Table 3).
Quantification in Metformin Drug Substance
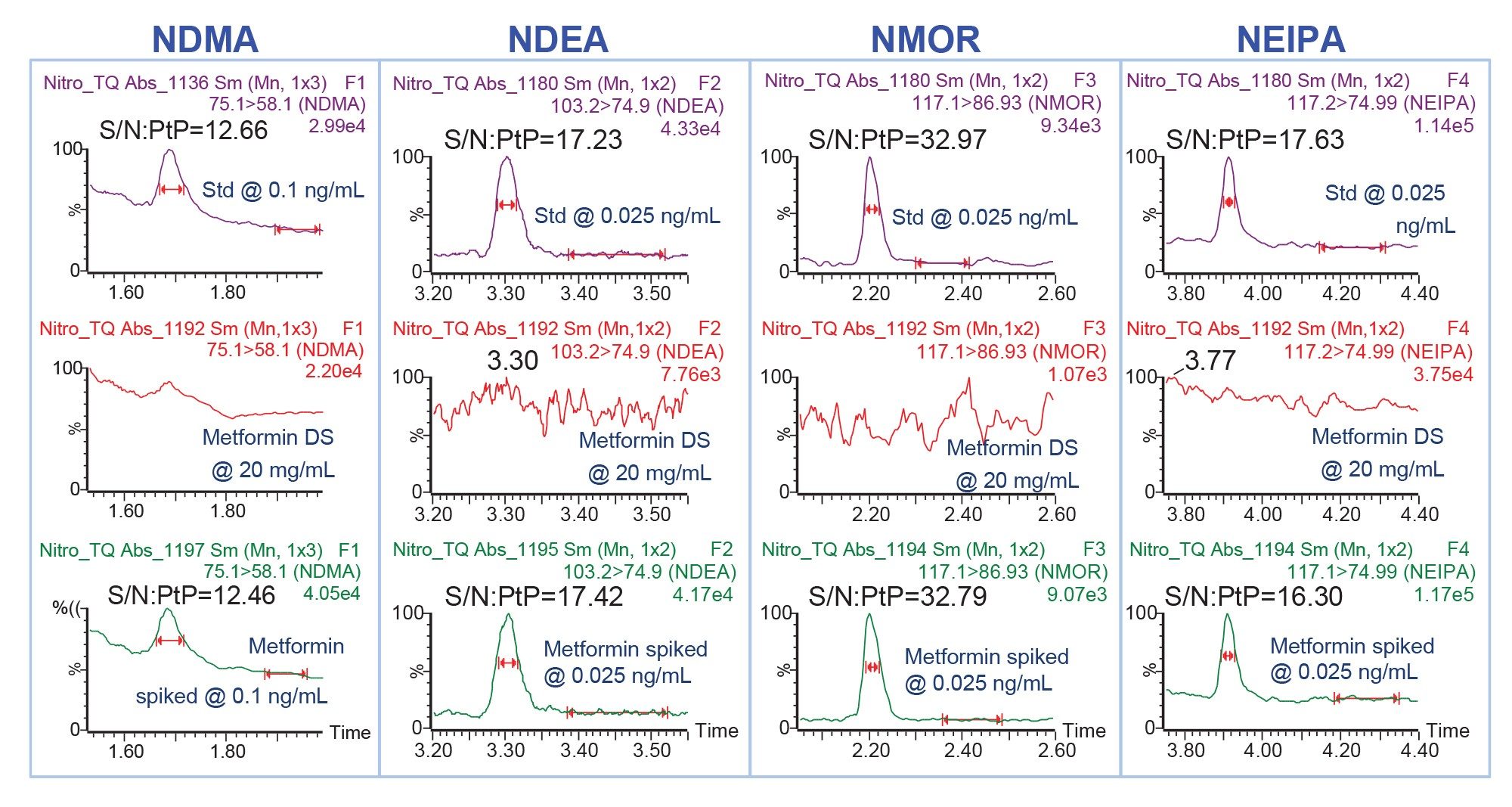
The metformin drug substance samples at 20 mg/mL in water were analyzed for the presence of nitrosamines using MRM acquisition mode. To assess method accuracy, the metformin samples were spiked with nitrosamines at 0.025, 0.1, and 1 ng/mL. This confirmed that the nitrosamine impurities can be accurately measured in the test samples containing high concentration of metformin. Representative chromatograms demonstrating analysis of nitrosamines (NDMA, NDEA, NMOR, and NEIPA) in metformin DS and in spiked metformin DS samples are shown in Figure 3. The analysis confirmed no detectable nitrosamines in the 20 mg/mL metformin drug substance samples tested in this work. Furthermore, the MS responses and S/N for nitrosamines in the metformin spiked samples were comparable to values in the neat standard solutions, indicating no ion suppression from the high concentration of the metformin peak.
The percent recovery was calculated using TargetLynx Software by comparing the calculated concentration against known spiked concentration. The calibration standards prepared in the metformin DS were used to calculate recoveries of nitrosamines. Using standards in the same matrix as the samples is generally recommended for accurate quantification. If the matrix contains analyte or interference, the standard addition method may be used.
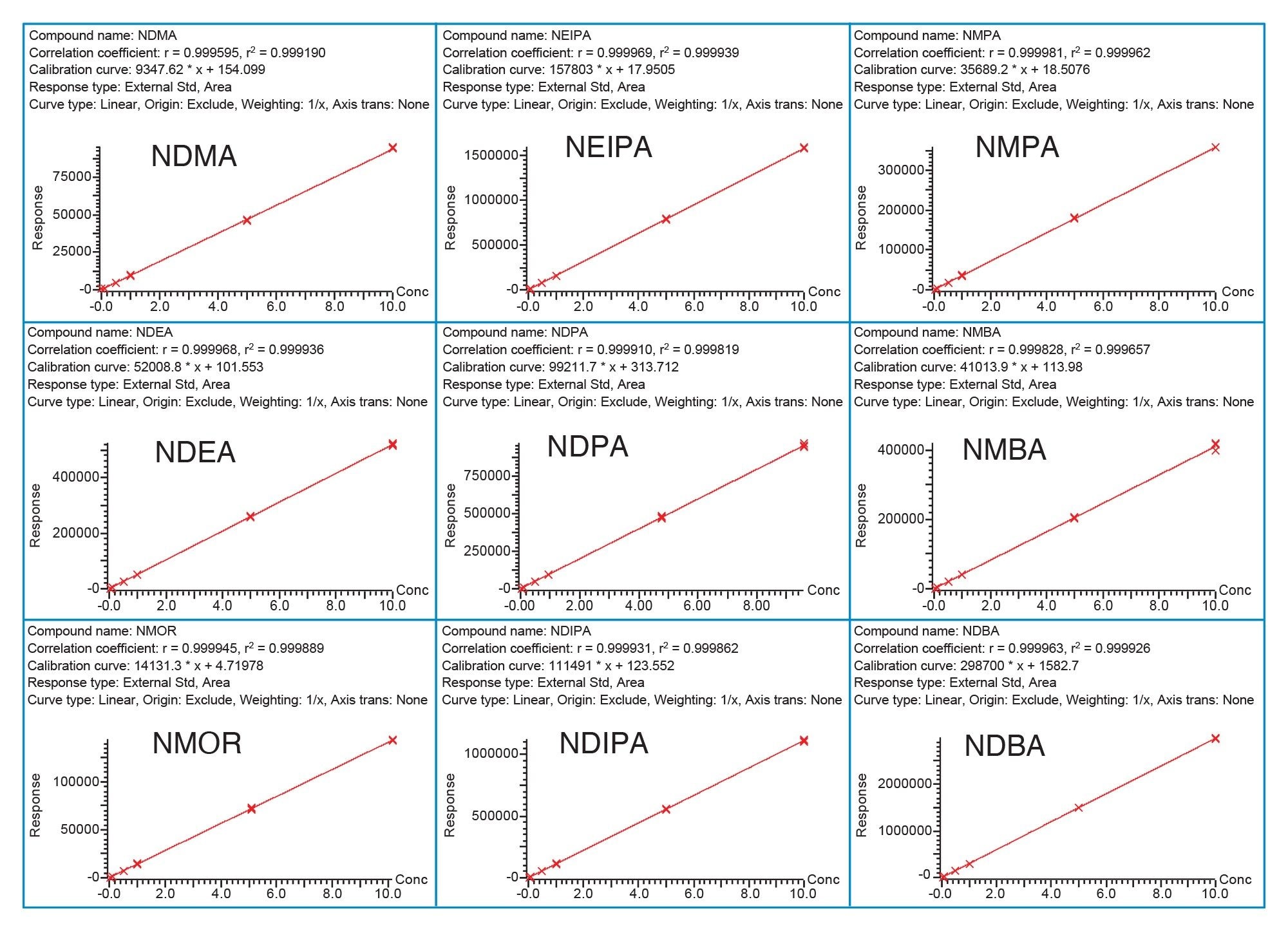
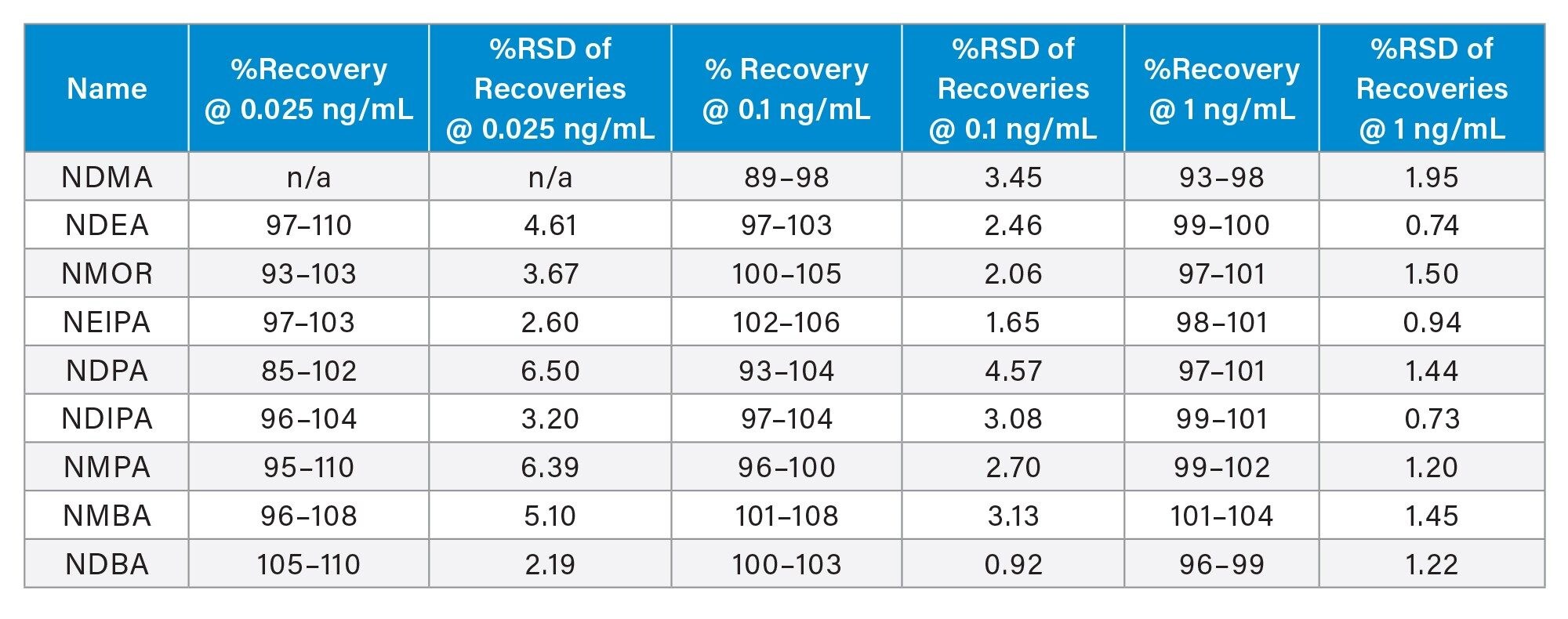
The calibration curves of nitrosamines standards in metformin DS exhibited linear relationship between MS responses and concentrations with R2 ≥ 0.999 (Figure 4). Excellent method accuracy was achieved for all nitrosamines in metformin drug substance (Table 4). For NDMA, the recovery at the 0.1 and 1 ng/mL ranged from 89 to 98% and 93 to 98%, respectively. For other impurities, recovery at the 0.025 ng/mL (or 0.00125 ppm relative to 20 mg/mL metformin drug substance) was between 85 and 110%, with RSD ≤ 6.50% for 5 sample preparations.
Conclusion
A highly sensitive method was developed for the ultra-low detection and quantification of nitrosamines in metformin drug substance, utilizing the Xevo TQ Absolute Mass Spectrometer with the ACQUITY Premier System. Excellent chromatographic separation was achieved using the Atlantis™ Premier BEH C18 AX Column. The method demonstrated excellent quantitative performance reaching LOQ limits of 0.01 to 0.1 ng/mL in neat solvent and 0.025 to 0.1 ng/mL in 20 mg/mL metformin drug substance, respectively. The linearity and accuracy of nitrosamines in metformin drug substance resulted in R2 ≥ 0.999 and recovery of 85 to 110%, respectively.
The described UPLC-MS/MS method offers highly sensitive, specific, and accurate analysis of nitrosamines in metformin drug substance, enabling fit-for-purpose accurate monitoring of nitrosamines at residual levels that are critical product quality and safety.
References
- ICH M7(R1) Assessment and Control of NDMA Reactive (Mutagenic) Impurities in Pharmaceuticals to Limit Potential Carcinogenic Risk, International Conference on Harmonization.
- G. Brambilla, A. Martelli, Genotoxic and Carcinogenic Risk to Humans of Drug–Nitrite Interaction Products, Mutat. Res. 635 (2007) 17–52.
- https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-alerts-patients-and-health-care-professionals-nitrosamine-impurity-findings-certain-metformin.
- FDA, Control of Nitrosamine Impurities in Human Drugs Guidance for Industry, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), February 2021.
- European Medicines Agency, Nitrosamine impurities in human medicinal products, Procedure number: EMEA/H/A-5(3)/1490, 25 June 2020.
- Parr MK and Joseph JF. NDMA impurity in valsartan and other pharmaceutical products: Analytical methods for the determination of N-nitrosamines. JPBA 2018;164(2019):536–549.
- Gushargi AJ and Halden RU. Critical Review of Major Sources of Human Exposure to N-nitrosamines. Chemosphere 2018;210:1124-1136.
- Lame ME, Lindsay H. High sensitivity quantification of Nitrosamines Genotoxic Impurities: LC-MS Analysis of Ranitidine Drug Product Using the Waters ACQUITY UPLC I-Class/Xevo TQ-XS Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer. Waters Application Note, 720006899, 2020.
720007725, September 2022